Posted by Kuniaki Saito, Student Researcher, Google Research, Cloud AI Team, and Kihyuk Sohn, Research Scientist, Google Research

Image retrieval plays a crucial role in search engines. Typically, their users rely on either image or text as a query to retrieve a desired target image. However, text-based retrieval has its limitations, as describing the target image accurately using words can be challenging. For instance, when searching for a fashion item, users may want an item whose specific attribute, e.g., the color of a logo or the logo itself, is different from what they find in a website. Yet searching for the item in an existing search engine is not trivial since precisely describing the fashion item by text can be challenging. To address this fact, composed image retrieval (CIR) retrieves images based on a query that combines both an image and a text sample that provides instructions on how to modify the image to fit the intended retrieval target. Thus, CIR allows precise retrieval of the target image by combining image and text.
However, CIR methods require large amounts of labeled data, i.e., triplets of a 1) query image, 2) description, and 3) target image. Collecting such labeled data is costly, and models trained on this data are often tailored to a specific use case, limiting their ability to generalize to different datasets.
To address these challenges, in “Pic2Word: Mapping Pictures to Words for Zero-shot Composed Image Retrieval”, we propose a task called zero-shot CIR (ZS-CIR). In ZS-CIR, we aim to build a single CIR model that performs a variety of CIR tasks, such as object composition, attribute editing, or domain conversion, without requiring labeled triplet data. Instead, we propose to train a retrieval model using large-scale image-caption pairs and unlabeled images, which are considerably easier to collect than supervised CIR datasets at scale. To encourage reproducibility and further advance this space, we also release the code.
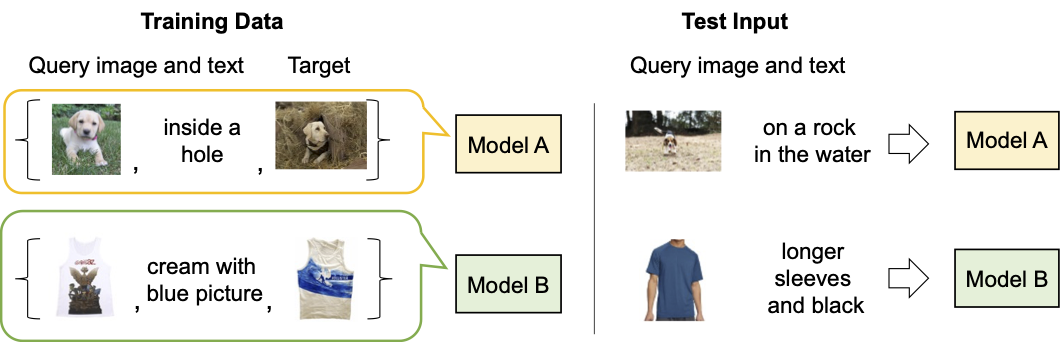 |
| Description of existing composed image retrieval model. |
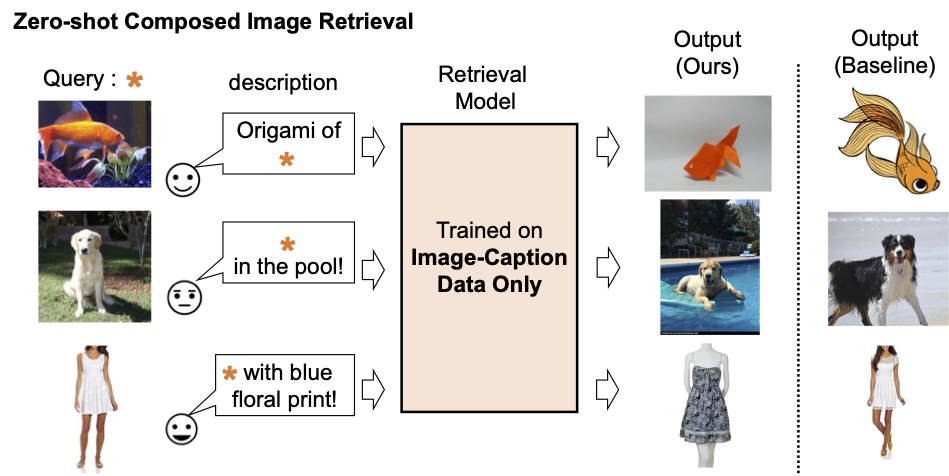 |
| We train a composed image retrieval model using image-caption data only. Our model retrieves images aligned with the composition of the query image and text. |
Method overview
We propose to leverage the language capabilities of the language encoder in the contrastive language-image pre-trained model (CLIP), which excels at generating semantically meaningful language embeddings for a wide range of textual concepts and attributes. To that end, we use a lightweight mapping sub-module in CLIP that is designed to map an input picture (e.g., a photo of a cat) from the image embedding space to a word token (e.g., “cat”) in the textual input space. The whole network is optimized with the vision-language contrastive loss to again ensure the visual and text embedding spaces are as close as possible given a pair of an image and its textual description. Then, the query image can be treated as if it is a word. This enables the flexible and seamless composition of query image features and text descriptions by the language encoder. We call our method Pic2Word and provide an overview of its training process in the figure below. We want the mapped token s to represent the input image in the form of word token. Then, we train the mapping network to reconstruct the image embedding in the language embedding, p. Specifically, we optimize the contrastive loss proposed in CLIP computed between the visual embedding v and the textual embedding p.
 |
| Training of the mapping network (fM) using unlabeled images only. We optimize only the mapping network with a frozen visual and text encoder. |
Given the trained mapping network, we can regard an image as a word token and pair it with the text description to flexibly compose the joint image-text query as shown in the figure below.
 |
| With the trained mapping network, we regard the image as a word token and pair it with the text description to flexibly compose the joint image-text query. |
Evaluation
We conduct a variety of experiments to evaluate Pic2Word’s performance on a variety of CIR tasks.
Domain conversion
We first evaluate the capability of compositionality of the proposed method on domain conversion — given an image and the desired new image domain (e.g., sculpture, origami, cartoon, toy), the output of the system should be an image with the same content but in the new desired image domain or style. As illustrated below, we evaluate the ability to compose the category information and domain description given as an image and text, respectively. We evaluate the conversion from real images to four domains using ImageNet and ImageNet-R.
To compare with approaches that do not require supervised training data, we pick three approaches: (i) image only performs retrieval only with visual embedding, (ii) text only employs only text embedding, and (iii) image + text averages the visual and text embedding to compose the query. The comparison with (iii) shows the importance of composing image and text using a language encoder. We also compare with Combiner, which trains the CIR model on Fashion-IQ or CIRR.
 |
| We aim to convert the domain of the input query image into the one described with text, e.g., origami. |
As shown in figure below, our proposed approach outperforms baselines by a large margin.
 |
| Results (recall@10, i.e., the percentage of relevant instances in the first 10 images retrieved.) on composed image retrieval for domain conversion. |
Fashion attribute composition
Next, we evaluate the composition of fashion attributes, such as the color of cloth, logo, and length of sleeve, using the Fashion-IQ dataset. The figure below illustrates the desired output given the query.
 |
| Overview of CIR for fashion attributes. |
In the figure below, we present a comparison with baselines, including supervised baselines that utilized triplets for training the CIR model: (i) CB uses the same architecture as our approach, (ii) CIRPLANT, ALTEMIS, MAAF use a smaller backbone, such as ResNet50. Comparison to these approaches will give us the understanding on how well our zero-shot approach performs on this task.
Although CB outperforms our approach, our method performs better than supervised baselines with smaller backbones. This result suggests that by utilizing a robust CLIP model, we can train a highly effective CIR model without requiring annotated triplets.
 |
| Results (recall@10, i.e., the percentage of relevant instances in the first 10 images retrieved.) on composed image retrieval for Fashion-IQ dataset (higher is better). Light blue bars train the model using triplets. Note that our approach performs on par with these supervised baselines with shallow (smaller) backbones. |
Qualitative results
We show several examples in the figure below. Compared to a baseline method that does not require supervised training data (text + image feature averaging), our approach does a better job of correctly retrieving the target image.
 |
| Qualitative results on diverse query images and text description. |
Conclusion and future work
In this article, we introduce Pic2Word, a method for mapping pictures to words for ZS-CIR. We propose to convert the image into a word token to achieve a CIR model using only an image-caption dataset. Through a variety of experiments, we verify the effectiveness of the trained model on diverse CIR tasks, indicating that training on an image-caption dataset can build a powerful CIR model. One potential future research direction is utilizing caption data to train the mapping network, although we use only image data in the present work.
Acknowledgements
This research was conducted by Kuniaki Saito, Kihyuk Sohn, Xiang Zhang, Chun-Liang Li, Chen-Yu Lee, Kate Saenko, and Tomas Pfister. Also thanks to Zizhao Zhang and Sergey Ioffe for their valuable feedback.


































